
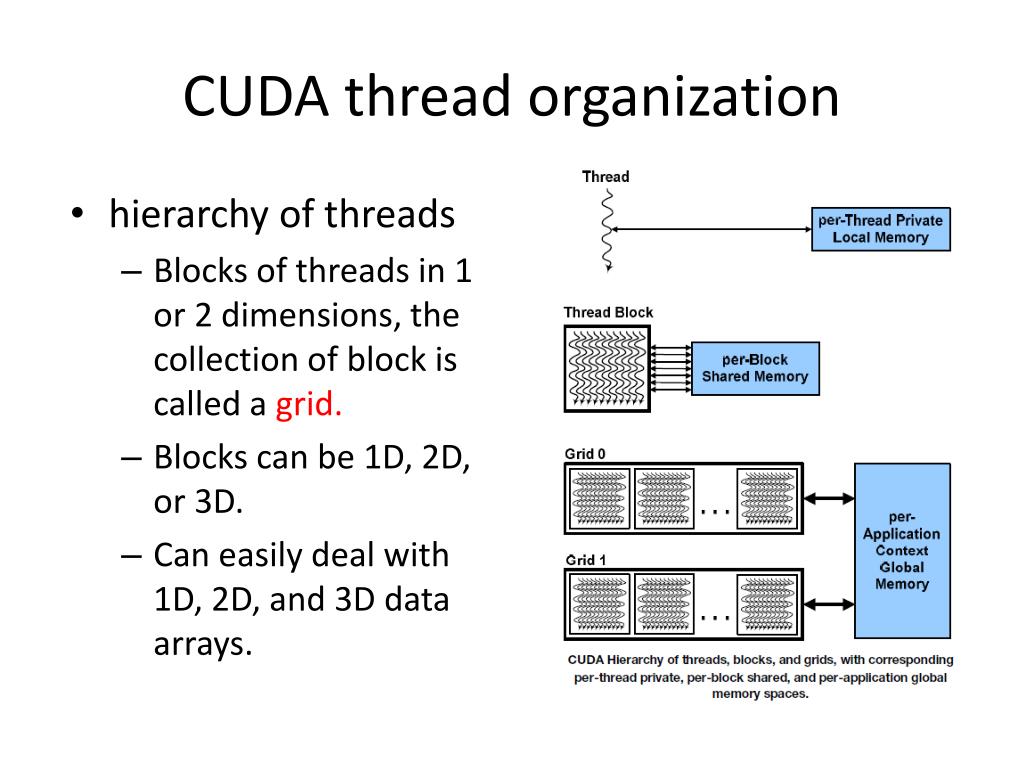
Furthermore, each thread executes the same kernel. This grid is divided into thread blocks, and each block is further divided into threads. In other words, each kernel function is executed in a grid of threads. This is a three-level thread hierarchy decomposed into threads, blocks of threads and grids of blocks, as shown in the figure below. CUDA exposes a thread hierarchy abstraction to enable you to organize your threads.
#DIM3 GRID CUDA HOW TO#
Knowing how to organize threads is a critical part of CUDA programming. Number of threads are generated and each thread executes the same statements specified by the kernel. Behind the scenes, CUDA schedules programmer-written kernels on GPU threads, i.e., when a kernel function is launched from the host, execution is moved to a device where a large As programmers, we write a kernel as a sequential program.
#DIM3 GRID CUDA CODE#
The most importantĬoncept to understand is the CUDA thread execution model that defines how kernels execute.Ī key component of the CUDA programming model is the kernel - the code that runs on the GPU device. Now is the time to learn its programming counterpart. We are already familiar with the GPU execution model (consisting of SMs, execution blocks, and warp scheduler) that executes and schedules thread blocks, threads and warps. Each SM consists of tens or hundreds of streaming processors (CUDA cores). Recall that a GPU device comprises several SMs. Runs on the host (usually, this is a desktop computer with a general-purpose CPU), and one or more kernels that run on GPU devices.

A GPU device is where the CUDA kernels execute. To one or more GPU accelerator devices, each with its own memory separated by a PCI-Express bus. A heterogeneous environment consists of CPUs complemented by GPUs, each with its own memory separated by a PCI-Express bus.Ī heterogeneous system consists of a single host connected The CUDA programming model enables you to execute applications on heterogeneous computing systems by simply annotating code with a set of extensions to the C programming language. A way to transfer data between CPU and GPU and access memory on the GPU.

Programming Graphics Processing Units (CUDA) Programming Graphics Processing Units (OpenCL)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
